1. 뷰
**뷰 만들 권한 부여
SQL> conn system/(비밀번호)
SQL> grant create view to scott;
**뷰 생성
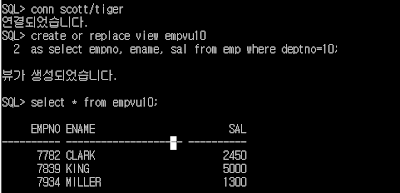
SQL> conn scott/tiger
SQL> create or replace view empvu10
2 as select empno, ename, sal from emp where deptno=10;
**뷰 사용
SQL> select * from empvu10;
**뷰 내용확인
SQL> desc user_views;
SQL> select view_name, text from user_views;
**뷰 테이블처럼 사용
SQL> select empno from empvu10;
SQL> select empno from empvu10 where empno=7782;
**뷰 생성 ---컬럼명을 지정해야함
SQL> create view salvu10
2 as select empno, ename, sal*12 //에러남
3 from emp where deptno=10;
SQL> create view salvu10
2 as select empno, ename, sal*12 year_sal //컬럼명 지정함
3 from emp where deptno=10;
**뷰 생성 ---다른방법
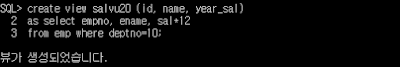
SQL> create view salvu20 (id, name, year_sal)
2 as select empno, ename, sal*12
3 from emp where deptno=10;
**뷰 생성 ---집계함수, 조인문장 포함된 복합뷰
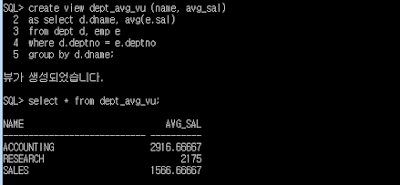
SQL> create view dept_avg_vu (name, avg_sal)
2 as select d.dname, avg(e.sal)
3 from dept d, emp e
4 where d.deptno = e.deptno
5 group by d.dname;
SQL> select * from dept_avg_vu;
**뷰 삭제
SQL> drop view salvu20;
**인라인 뷰 --이름이 없는 뷰 //select문을 괄호안에 씀
SQL> select * from (select empno, ename, sal from emp where deptno=10);
SQL> select d.dname, e.maxsal
2 from dept d, (select deptno, max(sal) maxsal
3 from emp
4 group by deptno) e
5 where d.deptno = e.deptno; //인라인 뷰를 조인에 활용함
**TOP-N 쿼리
//인라인 뷰를 사용함
//컬럼 값 중에서 가장 큰 값 또는 가장 작은 값 n 개를 질의하는 경우
SQL> select rownum, ename, sal
2 from (select ename, sal
3 from emp
4 order by sal desc)
5 where rownum <=5;
//조인문 포함 top-n쿼리
SQL> select rownum, e.ename, e.sal, d.loc
2 from dept d, (select ename, sal,deptno
3 from emp
4 order by sal desc) e
5 where e.deptno= d.deptno and rownum<=5;
2. 데이터베이스 객체
**시퀀스 --여러 사용자들이 공유하는 데이터베이스 객체로서 호출 될 때마다 중복되지 않은 고유한 숫자를 리턴하는 객체
//생성
SQL> create sequence emp_empno_seq
2 increment by 10
3 start with 10
4 maxvalue 100
5 nocache
6 nocycle;
//시퀀스 확인
SQL> desc user_sequences;
SQL> select sequence_name, min_value, max_value, increment_by, last_number
2 from user_sequences;
**NEXTVAL, CURRVAL 가상 컬럼 --가상 컬럼을 이용하여 시퀀스 번호를
검색할 수 있다.
SQL> select emp_empno_seq.nextval from dual;
SQL> select emp_empno_seq.currval from dual; //nextval로 불러와야지 사용가능
//시퀀스의 사용
---시퀀스에 의해 추출되는 번호는 순차적이지만, 시퀀스 번호는 COMMIT 또는
ROLLBACK 명령에 의해 지워지면 재사용 불가함, 공유번호이기 때문에 혼란방지
//시퀀스 변경
--해당 시퀀스의 소유자이거나 ALTER SEQUENCE 권한을 부여받아야 한다.
SQL> ALTER SEQUENCE EMP_EMPNO_SEQ
2 INCREMENT BY 2
3 MAXVALUE 9000
4 NOCACHE
5 NOCYCLE;
//시퀀스 삭제
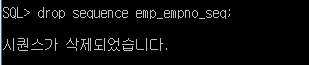
SQL> drop sequence emp_empno_seq;
3. INDEX
---행을 검색할 때 속도를 높이기 위해 Oracle 서버가 사용하는 스키마 객체
--경우에 따라서 데이터베이스가 인덱스를 검색하지 않을 수도 있음
**인덱스 생성
--PRIMARY KEY 또는 UNIQUE 제약조건을 지정하면 해당 컬럼에 고유 인덱스가 자동생성
--사용자가 필요에 따라 특정 컬럼에 별도의 인덱스를 생성
SQL> create index emp2_ename_idx on emp2(ename);
**인덱스 확인
SQL> select ic.index_name, ic.column_name,
2 ic.column_position, ix.uniqueness
3 from user_indexes ix, user_ind_columns ic
4 where ic.index_name = ix.index_name
5 and ic.table_name = 'EMP2';
**인덱스 삭제
SQL> drop index emp2_ename_idx;
**primary key로 인덱스 자동생성
SQL> alter table emp2
2 add constraint emp2_empno_pk primary key(empno);
//primary key를 삭제하면 인덱스도 사라짐
**함수 기반 인덱스
--인덱스가 생성된 컬럼이 함수에 입력되어 사용되면 절대 인덱스를 사용할 수 없다. 그래서 함수 기반 인덱스는 WHERE 조건의 함수 또는 연산식 자체를 인덱스로 생성한 것이다.
//권한부여
SQL> conn system/123456
SQL> grant query rewrite to scott;
//인덱스 생성
SQL> create index lower_job_idx
2 on emp2(lower(job));
4. 동의어 --객체에 대한 별칭
//권한 부여
SQL> grant create synonym to scott;
//생성
SQL> create synonym e for emp2;
//동의어 사용
SQL> select * from e where lower(ename)= 'smith';
//조회
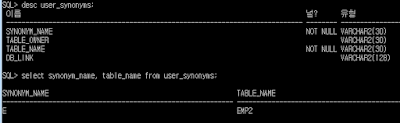
SQL> desc user_synonyms;
SQL> select synonym_name, table_name from user_synonyms;
//삭제
SQL> drop synonym e;
**공용동의어 public
---다른 사용자들도 같이 사용 할 수 있는 공용동의어가 생성된다. 관리자만 공용 동의어를 만들 수 있으며 다른 사용자들은 권한을 부여 받아야 한다.
//공용동의어 생성
SQL> create public synonym hr_emp for hr.employees;
//다른사용자 권한 부여
SQL> grant select on hr.employees to scott;
//다른사용자 동의어 접속
SQL> select * from hr_emp where first_name='Steven';
5. 사용자 접근 제어
--데이터베이스 보안은 시스템 보안과 데이터 보안으로 분류 할 수 있다. 시스템 보안은 사용자 계정 생성, 암호 변경, 디스크 공간 할당, 시스템 작업 등과 같이 시스템 수준에서의 데
이터베이스 접근 및 사용을 관리하는 것이며 데이터베이스 보안은 데이터베이스 객체에 대
한 사용자들의 접근 및 사용을 관리하는 것이다.
**사용자 생성
SQL> create user tom
2 identified by jerry; //생성후 해당 사용자 바로 접속 불가함
**접속권한 부여
SQL> grant create session to tom;
**테이블생성 권한 부여
SQL> grant create table to tom;
**테이블공간 사용 권한 부여
SQL> grant unlimited tablespace to tom;
**비밀번호 바꿈
SQL> alter user tom
2 identified by jerry; //관리자와 계정본인 둘다 가능함
**계정 잠금
SQL> alter user tom account lock;
**계정 잠금 해제
SQL> alter user tom account unlock;
**유저 조회
SQL> desc all_users;
SQL> select username, user_id created from all_users;
6. 객체 권한
--테이블 만든 사람이 권한을 줌
//상대방이 만든 객체에 접근
SQL> select * from scott.emp;
select * from scott.emp
//권한부여
SQL> grant select on emp to tom;
//재접근
//컬럼권한 부여
SQL> grant update (loc) on dept to tom;
//변경
SQL> update scott.dept set loc='뉴욕' where deptno=10;
SQL> update scott.dept set dname='회계' where deptno=10; //에러남
//권한 확인 --주는 쪽
SQL> select grantee, table_name, grantor, privilege
2 from user_tab_privs_made;
//권한 확인 --받는 쪽
SQL> select owner, table_name, grantor, privilege
2 from user_tab_privs_recd;
//권한 회수
SQL> revoke select on dept
2 from tom;
SQL> revoke select on emp
2 from tom;
7. 롤 ---권한을 하나하나 부여하는 것이 아니라 집합적으로 부여함
//롤 생성
SQL> create role newuser;
//롤에 권한 부여
SQL> grant create session, create table to newuser;
//사용자 생성
SQL> create user newuser1
2 identified by 123456;
//사용자에 롤 부여
SQL> grant newuser to newuser1;
//사용자 접속
C:\Users\user>sqlplus newuser1/123456
8. 데이터베이스 링크
---데이터베이스 링크를 사용함으로서 얻을 수 있는 가장 큰 장점은 로컬데이터베이스의 사용자들이 원격 데이터베이스내 객체에 접근하면 모든 권한은 해당 객체의 소유자 권한으로 한정된다는 점
//링크시킬 데이터생성
SQL> create table emp2 as select * from emp;
SQL> insert into emp2
2 values(8000,'RJU','MANAGER', 7934, sysdate, 2000, null, 40);
SQL> commit;
//접속경로 설정
//원격접속 확인
C:\Users\user>sqlplus scott@remote
//링크생성
SQL> conn system/123456
SQL> create public database link link3
2 connect to scott identified by tiger
3 using 'REMOTE';
//링크 연결
SQL> select * from emp2@link2 where empno=8000;
9. ROLLUP과 CUBE
--부분 집계에 사용되는 GROUP BY 절에 ROLLUP과 CUBE를 사용하면 다양한 통계 자료를
출력 할 수 있다
**ROLLUP
--ROLLUP은 GROUP BY에 의해서 출력되는 부분집계 결과에 누적된 부분 집계를 추가
SQL> select deptno, job, sum(sal)
2 from emp
3 group by rollup(deptno, job);
**CUBE
---CUBE는 뒤에 기술된 컬럼들에 대한 모든 조합을 그룹화하고, 각각의 그룹에 대하여
GROUP BY에 의해 부분집계를 수행
SQL> select deptno, job, sum(sal)
2 from emp
3 group by cube(deptno, job);
10. GROUPING 함수
--GROUPING 함수는 ROLLUP과 CUBE를 사용했을 때, 각각의 행들이 부분집계에 참여했는
지를 표시해준다
SQL> select deptno, job, sum(sal),
2 grouping(deptno),
3 grouping(job)
4 from emp
5 group by rollup(deptno, job);
//0을 리턴하는 경우 --해당 행이 집계 연산에 포함되었음.
11. GROUPING SETS
--GROUPING SETS는 GROUP BY를 확장한 것으로서 GROUPING SETS을 이용하면 사용자가 원하는 컬럼들로 구성된 그룹을 만들 수 있다
SQL> select deptno, job, mgr, sum(sal)
2 from emp
3 group by grouping sets
4 ((deptno,job,mgr),
5 (deptno,mgr),
6 (job,mgr));
12. 복수 컬럼 서브쿼리
**Pairwise 비교
SQL> select empno, job, deptno
2 from emp
3 where (job, deptno) in
4 (select job, deptno
5 from emp
6 where empno in (7369,7499))
7 and empno not in (7369,7499);
//사번이 7369 또는 7499번인 직원과 직급 및 부서코드가 동일한 사원 + 본인을 제외
**Nonpairwise 비교
SQL> select empno, job, deptno
2 from emp
3 where job in
4 (select job
5 from emp
6 where empno in (7369,7499))
7 and deptno in
8 (select deptno
9 from emp
10 where empno in (7369,7499))
11 and empno not in (7369,7499);
//사번이 7369 또는 7499번인 직원과 관리자사번이 같거나 직급이 같은 사원 +본인 제외
13. 상관관계 서브쿼리
---서브쿼리가 메인쿼리의 컬럼을 참조하도록 되어 있는 서브쿼리
SQL> select ename, sal
2 from emp e
3 where sal>(select avg(sal)
4 from emp
5 where e.deptno=deptno); //서브쿼리 안에 메인쿼리의 열이 들어가있음
**EXISTS
--서브쿼리의 결과가 한 개의 행이라도 존재하면 조건은 참이 되며 반대로 한 개
의 행도 존재하지 않으면 조건은 거짓
SQL> select empno, ename
2 from emp e
3 where exists (select 'X'
4 from emp
5 where e.empno = mgr);
14. WITH
-- 서브쿼리를 블럭으로 선언하여 문장의 다양한 위치에서 활용
SQL> with
2 dept_sal as (
3 select d.dname, sum(e.sal) as sal_sum
4 from dept d, emp e
5 where d.deptno = e.deptno
6 group by d.dname),
7 dept_avg as (
8 select avg(sal_sum) as sal_avg
9 from dept_sal)
10 select *
11 from dept_sal
12 where sal_sum>(select sal_avg
13 from dept_avg)
14 order by dname;
15. 계층형 쿼리
---위 그림과 같은 트리 구조의 데이터를 검색하는 방법이 계층형 쿼리
SQL> select empno, ename, mgr
2 from emp
3 start with ename= 'KING'
4 connect by prior empno=MGR;
**LEVEL
--계층형 쿼리에서 사용 할 수 있는 가상 컬럼 LEVEL은 트리 구조에서 계층을 나타낸다
SQL> select lpad(ename, length(ename) + (level*2)-2, ' ') name
2 from emp
3 start with ename = 'KING'
4 connect by prior empno = mgr;
16. 트리 구조의 노드(Node) 및 브랜치(Branch) 제거
//하향식 전개된 계층형 쿼리 결과에서 'FORD'를 제외하고 출력하려면
WHERE 절에서 제거할 노드를 제외 할 수 있는 조건을 기술해주면 된다
SQL> select lpad(ename, length(ename) + (level*2)-2, ' ') name
2 from emp
3 where ename != 'FORD'
4 start with ename='KING'
5 connect by prior empno = mgr;
//트리 구조에서 'FORD'의 브랜치를 제거하고 계층형 쿼리를 진행하고자 하는 경우에는 CONNECT BY씀
SQL> select lpad(ename, length(ename) + (level*2)-2, ' ') name
2 from emp
3 start with ename = 'KING'
4 connect by prior empno = mgr
5 and ename != 'FORD';
17


















































댓글 없음:
댓글 쓰기