- API 토큐먼트 문서를 모르면 프로그램 작성이 어려움
문제 해결을 위해서
- 검색
- 라이브러리 검색
- 문법적 지식
- 시스템 상황
- 현재 환경 설정
- 직접 적용 후 수정코딩 x
- 간단한 테스트 프로그램 실시 후 라이브러리 적용
- 재사용을 위해 정리를 해둠
- 프로그램 적용
2차원 배열 형식의 데이터 처리
- Data
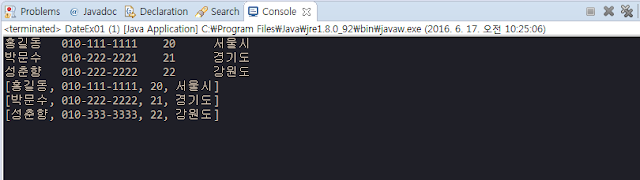
홍길동 010-111-1111 20 서울시
박문수 010-222-2222 21 경기도
성춘향 010-333-3333 22 강원도 - 프로그램에 저장
- 2차원 배열
API
- java.io
- 프로그램 내부로 데이터를 입력 / 출력
- input
- output
- 스트림
- 1byte
- 바이너리 / 영문자 / 숫자
- inputStream
- OutputStream
- 2byte
- 텍스트 (기타 국가 언어)
- Reader
- Writer
데이터
- 임시(휘발) 데이터
- 변수 / 상수
- 배열 / 컬렉션
- 영구 데이터
: 외부 저장장치에 담긴 데이터 - 로컬
- 파일
- 텍스트파일 : 메모장에서 열 수 있는 파일
- 바이너리파일 : 메모장에서 열 수 없음
- ex) jpg, mp3, mp4, ...
- 시스템
- 드라이브
- 디렉토리
- 파일속성
- 원격
- 데이터베이스
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class DateEx01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//2차원 배열
String[] data1 = {"홍길동", "010-111-1111", "20", "서울시"};
String[] data2 = {"박문수", "010-222-2221", "21", "경기도"};
String[] data3 = {"성춘향", "010-222-2222", "22", "강원도"};
String[][] datas = new String[3][];
datas[0] = data1;
datas[1] = data2;
datas[2] = data3;
//향상된 for 출력
for(String[] data : datas){
System.out.printf("%s \t %s \t %s \t %s \n", data[0], data[1], data[2], data[3]);
}
//arraylist로 처리
ArrayList<String> data11 =new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<String> data22 =new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<String> data33 =new ArrayList<>();
data11.add("홍길동");
data11.add("010-111-1111");
data11.add("20");
data11.add("서울시");
data22.add("박문수");
data22.add("010-222-2222");
data22.add("21");
data22.add("경기도");
data33.add("성춘향");
data33.add("010-333-3333");
data33.add("22");
data33.add("강원도");
ArrayList<ArrayList> al = new ArrayList<>();
al.add(data11);
al.add(data22);
al.add(data33);
for(ArrayList info : al){
System.out.println(info);
}
}
}2
public class Person {
private String name;
private String phone;
private String age;
private String region;
//constructor
public Person(String name, String phone, String age, String region) {
this.name = name;
this.phone = phone;
this.age = age;
this.region = region;
}
//getter
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public String getPhone() {
return phone;
}
public String getAge() {
return age;
}
public String getRegion() {
return region;
}
}import java.util.ArrayList;
public class DataEx03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//2차원 arraylist는 배열에 클래스를 넣는 것과 비슷한 개념
//1차원(열구분) 데이터
Person p1 = new Person("홍길동", "010-111-1111", "20", "서울시");
Person p2 = new Person("박문수", "010-222-2222", "21", "경기도");
Person p3 = new Person("성춘향", "010-333-3333", "22", "강원도");
// 2차원(행구분) 데이터
ArrayList<Person> a = new ArrayList<>();
a.add(p1);
a.add(p2);
a.add(p3);
// 향상된 for 출력
for(Person p : a){
System.out.printf("%s \t %s \t %s \t %s \n", p.getName(), p.getPhone(), p.getAge(), p.getRegion());
}
}
}
3
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.Date;
public class FileEx01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// File
File d1 = new File("c:\\java");
File f1 = new File("c:\\java\\test1.txt"); // 윈도우에서의 디렉토리 표현
File f2 = new File("c:/java/test.txt"); //리눅스 방식 디렉토리 표현
File f3 = new File("c:/java", "test.txt");
//존재 유무 탐색
if(f1.exists()){ //디렉토리도 특수목적 파일임으로 d1.exists() 존재유무를 검사 가능함
System.out.println("있음");
}else{
try {
f1.createNewFile(); //파일이 존재하지 않을 경우 test1.txt 파일을 생성
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("없음");
}
//파일 인지를 탐색
if(f1.isFile()){
System.out.println("파일");
}else{
System.out.println("디렉토리");
}
//isHidden() 숨김인지, canWrite() 쓰기가능한지, canRead() 읽을 수 있는지
if(f1.isHidden()){
System.out.println("숨김파일");
}else{
System.out.println("일반파일");
}
//경로
try {
System.out.println(f1.getName());
System.out.println(f1.getPath()); //현재파일 경로
System.out.println(f1.getCanonicalPath()); //상대경로
System.out.println(f1.getParent()); //상위폴더 경로
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//파일의 크기
System.out.println(f1.length()+ "Byte"); //숨김파일이라서 0Byte 나옴
System.out.println(f2.length()+ "Byte");
//생성시간
System.out.println(f1.lastModified()); //1970년 1월 1일 부터 현재까지 밀리세컨드 단위로 환산시간 Unixdate
System.out.println(new Date(f1.lastModified()).toLocaleString()); //Date API통해서 현재 시간으로 바꿈
Calendar c = Calendar.getInstance(); //Calendar API통해서 만듦
c.setTimeInMillis(f1.lastModified());
System.out.println(c.get(Calendar.YEAR)+"년 " +c.get(Calendar.MONTH)+"월 "+ c.get(Calendar.DATE)+"일");
}
}4
import java.io.File;
public class FileEx02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//디렉토리 내부의 목록접근
File f1 = new File("c:/");
//배열로 받음
/* String[] lists = f1.list();
for(String list : lists){
System.out.println(list);
}*/
//File클래스로 받음 //File 메소드로 파일타입 검사후 디렉토리 경우 괄호
File[] listFiles = f1.listFiles();
for(File listFile : listFiles){
if(listFile.isFile()){
System.out.println(listFile.getName());
}else{
System.out.printf("[%s] \n", listFile.getName());
}
}
}
}5
import java.io.File;
public class FileEx03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 디렉토리 생성
File f = new File("c:/java/dire");
if(f.mkdir()){ //make directory
System.out.println("성공");
}else{
System.out.println("실패");
}
//디렉토리 삭제
if(f.delete()){ //delete 디렉토리와 파일의 삭제를 다 함
System.out.println("성공");
}else{
System.out.println("실패");
}
//이름 변경 renameTo
}
}6
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
public class FileEx04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 파일읽기
FileInputStream fis = null;
try {
fis = new FileInputStream("c:/java/test.txt"); //new를 쓰면 파일이 열린체로 있음, 에러가 나면 파일이 깨짐
// int data = fis.read(); //read는 한글짜씩 읽음 ASCII코드로 읽음
// System.out.println("데이터 : "+ (char)data);
// data = fis.read();
// System.out.println("데이터 : "+ (char)data);
int data = 0;
while((data = fis.read()) != -1){ //fit.read()는 마지막까지 읽으면 -1을 리턴함
if(data == '\r'){ //엔터키의 ASCII code도 읽어드림 (window \r \n) (linux \n)
System.out.print("(r)");
}else if(data == '\n'){
System.out.print("(n)");
}else{
System.out.print((char)data); //1byte 방식으로 읽어서 한글깨짐
}
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) { //파일을 찾지 못했을 경우 exception
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
fis.close(); //에러유무와 관계없이 프로르램 끝에 파일을 닫아줌
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}7
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class FileEx05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 파일 쓰기
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try {
fos = new FileOutputStream("c:/java/newtest.txt");
fos.write('a'); //파일글쓰기
fos.write('b');
fos.write('c');
System.out.println("출력 완료");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally{
try {
fos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
8
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class FileEx06 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 이미지 복사
FileInputStream fis = null;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try {
fis = new FileInputStream("c:/java/Koala.jpg"); //읽을 파일
fos = new FileOutputStream("c:/java/newKoala.jpg"); //쓸 파일
int data= 0;
while((data =fis.read()) != -1){ //읽는 것과 동시에 쓰기
fos.write(data);
}
System.out.println("복사 완료");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try { fos.close(); } catch (IOException e) {}
try { fis.close(); } catch (IOException e) {}
}
}
}
9
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
public class FileEx07 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Buffered // 2차 스트림 // 처리속도가 더 빠름
BufferedInputStream bis = null;
FileInputStream fis = null;
try {
//fis = new FileInputStream("c:/java/test.txt");
//bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis); //1차 스트림을 통해서 만들수 있음
bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("c:/java/test.txt")); //fis 객체를 열지 않아도 됨
int data = 0;
while((data = bis.read()) != -1){
System.out.print((char)data);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(bis != null) try{ bis.close(); } catch(IOException e){}
//if(fis != null) try{ fis.close(); } catch(IOException e){}
}
}
}
10
import java.io.BufferedOutputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class FileEx08 {
//Buffered 2차 스트림 쓰기
public static void main(String[] args) {
BufferedOutputStream bos = null;
try {
bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("c:/java/test123.txt"));
bos.write('a'); bos.write('b'); bos.write('c');
bos.write('\r'); bos.write('\n');
bos.write('a'); bos.write('b');
bos.write('\n');
bos.write('c');
System.out.println("출력 완료");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(bos != null) try{ bos.close();} catch(IOException e){}
}
}
}
11
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.io.BufferedOutputStream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class BufferedEx {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 2차 스트림 이미지 복사 //빠른 속도로 복사됨
BufferedInputStream bis = null;
BufferedOutputStream bos = null;
try {
bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("c:/java/Koala.jpg"));
bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("c:/java/buffered_Koala.jpg"));
int data =0;
while((data = bis.read()) != -1){
bos.write(data);
}
System.out.println("복사완료");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(bis != null) try{ bis.close(); } catch(IOException e){}
if(bos != null) try{ bos.close(); } catch(IOException e){}
}
}
}
12
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
public class FileEx10 {
//FileReader //2byte 파일 읽기
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileReader fr = null;
try {
fr = new FileReader("c:/java/test.txt");
int data= 0;
while((data = fr.read()) != -1){
System.out.print((char)data);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(fr != null) try{ fr.close();} catch(IOException e){}
}
}
}13
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
public class FileEx11 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// buffered 2byte 읽기
BufferedReader br = null;
try {
br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("c:/java/test.txt"));
/* int data= 0;
while((data = br.read()) != -1){
System.out.print((char)data);
*/
String data = null;
while((data = br.readLine()) != null){ //readLine은 한줄씩 읽어올 수 있음 //다 읽으면 null값 반환
//엔터까지 읽고나서 엔터는 출력하지 않음
System.out.println(data); //println통해서 엔터 추가해줘야함
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(br != null) try{ br.close();} catch(IOException e){}
}
}
}
14
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
public class FileEx12 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//bufferedWriter 2차 스트림 쓰기
BufferedWriter bw = null;
try {
bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("c:/java/test_BufferedWrite.txt"));
bw.write("Hello World\r\n");
bw.write("Hello World\r\n");
bw.write("Hello World\r\n");
System.out.println("출력완료");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(bw != null) try{ bw.close();} catch(IOException e){}
}
}
}
15
import java.io.*;
class FileEx13_sub implements Serializable{
int x;
int y;
}
public class FileEx13 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 글자가 아니라 object 전체를 쓰기
FileEx13_sub ap = new FileEx13_sub();
ap.x = 100;
ap.y =200;
File dir = new File("c:/java");
File file = new File(dir, "object.txt"); //디렉토리와 파일을 분리해서 경로를 작성하는 방법
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file);
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos);
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(bos);
oos.writeObject(ap);
oos.close();
//만약 객체단위의 출력을 하지 못한다면 다음과 같이 출력해야함
/*
File f = new File("aaa.txt");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(f);
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos);
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(bos);
oos.writeInt(ap.x);
oos.writeInt(ap.y);
oos.close();
*/
}
}
16
import java.io.*;
public class FileEx14 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// object전체를 읽기
File file = new File("c:/java/object.txt");
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(file)));
Object obj = null;
try {
obj = ois.readObject();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
ois.close();
}
FileEx13_sub ap = (FileEx13_sub)obj;
System.out.println("x = " + ap.x);
System.out.println("y = " + ap.y);
}
}
17
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
public class FileEx15 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// System.in 통해서 keyboard입력
//InputStreamReader isr = null; //2byte 한글 읽음
//InputStream is = null; //1byte 읽음
BufferedReader br = null; //여러줄 읽음
try {
//is = System.in;
//isr = new InputStreamReader(is);
//br = new BufferedReader(isr);
br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); //한줄로 초기화
System.out.println("데이터 입력 : ");
/*System.out.println("입력값 : " + (char)isr.read()); //한글자씩 읽음
System.out.println("입력값 : " + (char)isr.read());
System.out.println("입력값 : " + (char)isr.read());*/
System.out.println("입력값 : " + br.readLine());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(br != null) try{ br.close(); } catch(IOException e){ }
}
}
}
18
import java.io.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class Read {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//읽어서 쪼갠뒤에 리스트에 저장
BufferedReader datas = null;
ArrayList<ArrayList> all = new ArrayList<>(); //주소행처리 all 리스트 만듬
try {
datas = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("c:/java/zipcode_seoul_utf8.csv")); //파일읽음
String data = null; //한줄읽을 변수 만듦
while((data = datas.readLine()) != null){
ArrayList<String> al = new ArrayList<>(); //주소열처리 al리스트 만듦
String[] arr = data.split(","); //주소열 처리 al 어래이 만듦
//데이터를 집어넣음 값이 없으면 스패이스바를 넣음
for(int i=0;i<7;i++){
if(arr[i].equals("")){
al.add(" ");
}else{
al.add(arr[i]);
}
}
all.add(al);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(datas != null) try{ datas.close();} catch(IOException e){}
}
// 동이름 입력
BufferedReader br = null;
String dong = null;
try {
while(true){
br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
System.out.println("동이름 입력 : ");
dong = br.readLine();
//입력값이 exit이면 반복문 나오기
if(dong.equals("exit")){
break;
}else{
//리스트에 것을 검색 하고 출력
for(ArrayList al : all){
if(((String)al.get(3)).indexOf(dong) != -1){
System.out.printf("[%s] \t %s \t %s \t %s \t %s \t %s \n",al.get(0),al.get(1),al.get(2),al.get(3),al.get(4),al.get(5));
}
}
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(br != null) try{ br.close(); } catch(IOException e){ }
}
}
}19
주소검색 코드만들기2 (객체지향적으로)
import java.io.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
//데이터만 처리하는 bean클래스 만들기
public class DataSet {
//읽어서 쪼갠뒤에 리스트에 저장
ArrayList<ArrayList<String>> all = new ArrayList<>();
//생성자에서 매소드를 실행시켜 멤버변수를 채움
public DataSet(){
this.DataRead();
}
public void DataRead() {
BufferedReader datas = null;
try {
datas = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("c:/java/zipcode_seoul_utf8.csv")); //파일읽음
String data = null; //한줄읽을 변수 만듦
while((data = datas.readLine()) != null){
ArrayList<String> al = new ArrayList<>(); //주소열처리 al리스트 만듦
String[] arr = data.split(","); //주소열 처리 al 어래이 만듦
//데이터를 집어넣음
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
al.add(arr[i]);
}
all.add(al);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(datas != null) try{ datas.close();} catch(IOException e){}
}
}
}import java.io.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Search {
DataSet dataset = new DataSet(); //데이터클래스 불러오기
BufferedReader br = null; //finally에서 끄기위해서 메소드 밖에 선언함
//검색 메소드 만들기
public void SearchMethod() throws Exception{
while(true){
br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); //입력값 받기
System.out.println("동이름 입력 : ");
String dong = br.readLine();
//입력값이 exit이면 반복문 나오기
if(dong.equals("exit")){
break;
}else{
//리스트에 것을 검색 하고 출력
for(ArrayList<String> al : dataset.all){
if(al.get(3).indexOf(dong) != -1){
System.out.printf("[%s] \t %s \t %s \t %s \t %s \t %s \n",al.get(0),al.get(1),al.get(2),al.get(3),al.get(4),al.get(5));
}
}
}
}
}
//Main 부분
public static void main(String[] args) {
Search search =new Search();
try {
search.SearchMethod();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(search.br != null) try{ search.br.close(); } catch(IOException e){ }
}
}
}

















댓글 없음:
댓글 쓰기