- 자료형
- 기본자료형
- 논리형
- 숫자형
- 문자형
- 확장자료형
- 문자열형
- 흐름
- 조건(분기)
- 삼항연산자
(조건)? 실행문: 거짓일때 실행문; - 반복
- for
for(초기식; 비교식; 증감식){ 실행문 } - 유한루프 위주 사용 (프로그래머가 시작과 끝을 알고 있을 때)
- while
초기식; while(비교식){ 실행문; 증감식; } - 무한루프 위주 사용
- do ~ while
초기식 do{ 실행문 } while( 비교식 ) - 기타 예약어
- break : 반복문의 중단
- continue : 반복문 한번 건너 뜀
- 흐름의 중쳡 → 알고리즘
- 에러 : 수치오류 /속도
Java 배열
- 배열: 변수 하나에 값을 여러개 할당하는 자료형
- 값을 구분하는 인자: Index
- 선언
- int[] ar1;
- int ar1[];
- 미리 예약 (데이터받는 갯수 정하기)
- ar1 = new int[4]
- 초기화
- ar1 = [1, 2, 3, 4];
- 데이터 접근
- ar1[0] : 인덱스는 반드시 0부터 시작함
- ar1[1]
- ar1[2]
Java 자료형
- 기본 자료형
- int a =1;
- 램에서 4byte를 차지하고 그 부분을 a라고 부르고 데이터를 넣는다.
- 참조(확장) 자료형
- int[] a = new int[4];
- new가 있으면 확장 자료형
- 램(stack)에서 4byte를 차지하고 그 부분을 a라고 부르고 데이터 주소 지정.
- 램에서 데이터를 넣는 부분(constant)을 따로 4개 각각 4byte 만든다.
객체와 클래스
- 객체 (설계) : 사물의 원형의 모습을 이야기함
- 객체모델링: 객체간의 관계를 그려주는 것 (프로그램 : UML, 전문가: 아키텍처)
- 다이어그램: 모델링 그림
- class (기술) : 새로운 자료형
- API / Library : oracle에서 만들어 둔 class
- Member : 클래스의 구성요소
- Field : 변수
- Method : 함수
- Nested Class : 중첩 클래스
- Construct : 생성자
객체 클래스 예시
- 객체 (ex학생)
- 학번
- 이름
- 나이
- 키
- 클래스
- class Student {
int number;
String name;
int age;
double height;
}
Java 동영상 강의
- http://www.wiz.center
- http://tryhelloworld.co.kr
public class ConditionEx01{
public static void main(String[] args){
//삼항연산자
char c1=(10>3)?'a':'b';
System.out.println(c1);
char c2=(10<3)?'a':'b';
System.out.println(c2);
}
}2
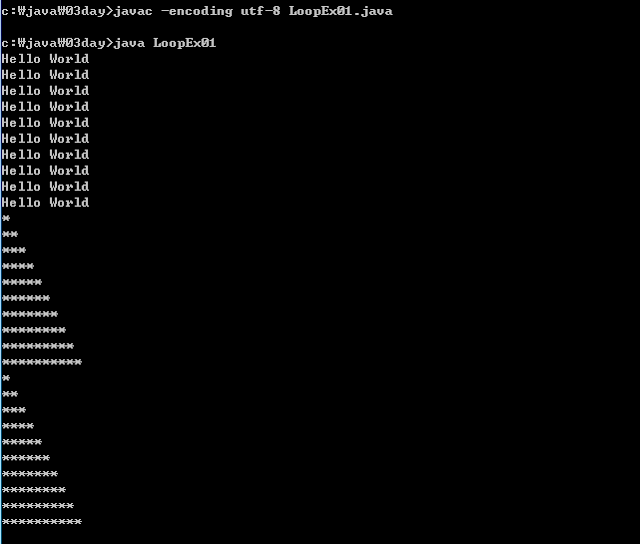
public class LoopEx01{
public static void main(String[] args){
//반복문 while
int i = 1; //초기식
while(i<=10){ //비교식
System.out.println("Hello World");
i++; //증감식
}
//while문 별표 피라미드
int j=1;
while(j<=10){
int k=1;
while(k<=j){
System.out.print("*");
k++;
}
System.out.println();
j++;
}
//while 문 별표 피라미드
int l=1;
String sum="";
while(l<=10){
int m=1;
while(m<=l){
sum +="*";
m++;
}
sum += "\n";
l++;
}
System.out.println(sum);
}
}3
public class LoopEx02{
public static void main(String[] args){
//반복문 do while
int i=1;
do{
System.out.println("Hello World");
i++;
}while(i<=10);
}
}4
public class LoopEx03{
public static void main(String[] args){
//기타예약어 break, continue
//break
System.out.println("시작");
int n=0;
while(n<10){
n++;
if(n==5){
break; // 5일때 모든 반복문 종료
}
System.out.println(n);
}
System.out.println("종료");
//continue
System.out.println("시작");
n=0;
while(n<10){
n++;
if(n==5){
continue; //5일때 현재 반복문 건너뜀
}
System.out.println(n);
}
System.out.println("종료");
}
}5
public class LoopEx04{
public static void main(String[] args){
//break
int n1=0;
one: //라벨 붙이기
while(n1<=5){
n1++;
int n2=0;
while(n2<=5){
n2++;
if(n2==3){
break one; //break는 자신을 감싸고 있는 반복문에만 영향을 미친다
//자신이 원하는 위치까지 종료범위를 정하고 싶으면 라벨을 붙인다.
}
System.out.println(n1+" : " + n2);
}
}
System.out.println("종료");
}
}6
public class ArrayEx01{
public static void main(String[] args){
//배열의 선언
//정수형 자료형 여러개 받을 수 있는 배열 선언
int[] ar1;
//받을 수 있는 자료의 갯수 선언
ar1 = new int[4];
//값을 초기화
ar1[0]=10;
ar1[1]=20;
ar1[2]=30;
ar1[3]=40;
System.out.println(ar1[0]);
System.out.println(ar1[1]);
System.out.println(ar1[2]);
System.out.println(ar1[3]);
//확장자료형의 이해
//int ar1 = 1; 기본자료형 ---램의 한곳에 변수명과 데이터를 둘다 저장
//int[] ar1; ar1 = new int[4] 확장자료형 --램의 한곳에 데이터 이름과 주소를 램의 다른곳에 데이터를 저장
System.out.println(ar1); //ar1에는 데이터가 아닌 데이터가 있는 주소가 담겨있다
int[] ar2 = ar1; //ar2에 주소를 할당함
System.out.println(ar2[0]); //ar2로 ar1으로 만들어놓은 데이터 위치를 불러온다
ar2[0]=100; // ar2에서 데이터를 변경하면 ar1, ar2둘다 바뀐다.
System.out.println(ar2[0]);
System.out.println(ar1[0]);
}
}7
public class ArrayEx02{
public static void main(String[] args){
//배열의 선언
int arr1;
int arr2[];
//데이터 메모리 선언
arr1 = new int[5];
arr2 = new int[5];
//배열과 데이터메모리 선언
int[] arr3 = new int[5];
//데이터 초기화
arr[0]=10;
//선언과 초기화
int[] arr4={10,20,30,40};
int[] arr4=new int[]{10,20,30,40};
}
}8
public class ArrayEx03{
public static void main(String[] args){
//배열
int[] arr1 = {10, 20, 30, 40};
// System.out.println(arr1[0]);
// System.out.println(arr1[1]);
// System.out.println(arr1[2]);
// System.out.println(arr1[3]);
System.out.println(arr1.length); //배열의 공간 수
for(int i=0; i<arr1.length; i++){
System.out.println(arr1[i]);
}
// 향상된 for //데이터를 뽑아냄
for(int data : arr1){
System.out.println("데이터 : "+ data);
}
}
}9
public class ArrayEx04{
public static void main(String[] args){
//배열
String[] fruits= {"사과","수박", "딸기"};
for(String fruit : fruits){
System.out.println("과일 : "+ fruit);
}
}
}10
public class ArrayEx05{
public static void main(String[] args){
int[] arr;
//System.out.println(arr.length); //컴파일시 에러남
//System.out.println(arr[0]); //컴파일시 에러남
arr = new int[5];
arr[0] =10;
//arr[10] =10; //지정된 배열 범위를 넘어섬 //컴파일된 클래스파일 실행시 에러남
}
}11
public class ArrayEx06{
public static void main(String[] args){
int[][] arr;
//2차원 배열
//3행 2열 : 6개 의방
arr = new int[3][2];
//3개를 먼저 만들고 각각 2개의 주소를 받음
arr[0][0]=10;
arr[0][1]=20;
arr[1][0]=30;
arr[1][1]=40;
arr[2][0]=50;
arr[2][1]=60;
System.out.println(arr[0][0]);
System.out.println(arr[2][1]);
System.out.println(arr.length); // 2차원 array은 갯수 세는것이 애매함
System.out.println(arr[0]); //배열안에 배열이 들어가 있기 때문에 주소가 출력됨
System.out.println(arr[1]);
System.out.println(arr[2]);
//2차원 배열의 모든 데이터 출력
for(int row=0; row<arr.length; row++){
for(int col=0; col<arr[row].length; col++){
System.out.println("데이터 : "+ arr[row][col]);
}
}
//향상된 for문
for(int[] datas : arr){ //배열을 읽어 드림
for(int data : datas){ //데이터를 읽음
System.out.println("data : "+data);
}
}
}
}12
public class ArrayEx07{
public static void main(String[] args){
//2차원 배열
//int[][] arr1 = {{10,20},{30,40},{50,60}};
int[][] arr1 = new int[][]{{10,20},{30,40},{50,60}};
for(int[] datas : arr1){
for(int data : datas){
System.out.println("데이터 : "+data);
}
}
}
}13
public class ArrayEx08{
public static void main(String[] args){
//2차원 배열 각 배열 공간 다르게
int[][] arr = new int[3][];
arr[0]=new int[3];
arr[1]=new int[2];
arr[2]=new int[1];
arr[0][0]=10;
arr[0][1]=20;
arr[0][2]=30;
arr[1][0]=40;
arr[1][1]=50;
arr[2][0]=60;
int[][] arr2 = {{10,20,30},{40,50},{60}};
for(int row=0; row<arr.length; row++){
for(int col=0; col<arr[row].length; col++){
System.out.println("데이터 : "+ arr[row][col]);
}
}
}
}14
public class ArrayEx10{
public static void main(String[] args){ //args 프로그램 실행시 문자열로 외부데이터 읽어옴
//java ArrayEx10 1 1
//결과 +
/*
String data1 = args[0];
String data1 = args[1];
System.out.println("덧셈 : "+data1 + data2); //문자열 덧셈이 됨
*/
// String -> int : Integer.parseInt(문자열)
int data1=Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
int data2=Integer.parseInt(args[1]);
System.out.println("덧셈 : "+(data1 + data2));
}
}15
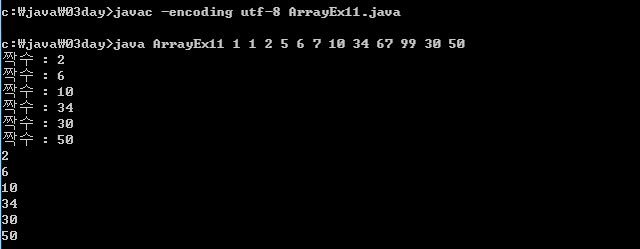
public class ArrayEx11{
public static void main(String[] args){
//입력 값이 짝수 일때 내보내기
for(int i=0;i<args.length;i++){
if(Integer.parseInt(args[i])%2==0){
System.out.println("짝수 : "+args[i]);
}
}
//향상된 for 문으로 짝수 찾기
for(String data: args){
if(Integer.parseInt(data)%2==0){
System.out.println(data);
}
}
}
}16
//클래스 선언
//Student라는 새로운 자료형 선언
class Student {
int hakbun;
String name;
int age;
double height;
}
public class ObjectEx01{
public static void main(String[] args){
int a;
a=10;
System.out.println(a);
// 배열의 메모리 구조와 같음
// s1 : 참조(객체)변수, instance
Student s1;
s1 = new Student(); //new 메모리 할당 연산자
System.out.println(s1); //주소가 출력됨
//. 객채 참조 연산자
s1.hakbun = 1111;
s1.name = "홍길동";
s1.age = 20;
s1.height = 180.1;
System.out.println(s1.hakbun);
System.out.println(s1.name);
// 참조변수를 여러개 만들 수 있음
Student s2 = new Student();
s1.hakbun = 1112;
s1.name = "박문수";
s1.age = 25;
s1.height = 185.1;
System.out.println(s1.hakbun);
System.out.println(s1.name);
}
}17
// 동일디렉토리에 내에 호출해야하는 Student 클래스 파일이 있으면
// Object.java 컴파일시
// Object.java Student.java 둘다 컴파일함
public class ObjectEx01{
public static void main(String[] args){
Student s1;
s1 = new Student();
System.out.println(s1);
s1.hakbun = 1111;
s1.name = "홍길동";
s1.age = 20;
s1.height = 180.1;
System.out.println(s1.hakbun);
System.out.println(s1.name);
}
}//클래스 선언
class Student {
int hakbun;
String name;
int age;
double height;
}18
public class ObjectEx02{
public static void main(String[] args){
Student s1 = new Student();
s1.hakbun = 1111;
s1.name = "홍길동";
s1.age = 20;
s1.height = 180.1;
System.out.println(s1); //Student(클래스명)@15db9742(주소)
//주소복사
Student s2=s1; //인스턴스 값을 받음
System.out.println(s2);
System.out.println(s2.name);
s2.name ="박문수"; //데이터 값을 바꾸면 s1, s2 둘 모두 데이터가 바뀜
System.out.println(s1.name);
System.out.println(s2.name);
}
}19
public class ObjectEx03{
public static void main(String[] args){
Student s3;
//new를 하지 않았으므로 메모리가 생성되지 않았음, field에 접근 할 수 없음
System.out.println(s3.name);
}
}

















댓글 없음:
댓글 쓰기