import java.awt.EventQueue;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JPanel;
import javax.swing.border.EmptyBorder;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import java.awt.event.MouseAdapter;
import java.awt.event.MouseEvent;
import java.util.Timer;
import java.util.TimerTask;
public class Test2 extends JFrame {
JButton btnNewButton;
private JPanel contentPane;
/**
* Launch the application.
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
EventQueue.invokeLater(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
try {
Test2 frame = new Test2();
frame.setVisible(true);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}
/**
* Create the frame.
*/
public Test2() {
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
setBounds(100, 100, 450, 300);
contentPane = new JPanel();
contentPane.setBorder(new EmptyBorder(5, 5, 5, 5));
setContentPane(contentPane);
contentPane.setLayout(null);
btnNewButton = new JButton("New button");
btnNewButton.addMouseListener(new MouseAdapter() {
@Override
public void mouseEntered(MouseEvent e) {
int x = (int)(Math.random()*300);
int y = (int)(Math.random()*200);
System.out.println(x+"//"+y);
Timer timer = new Timer(true);
timer.scheduleAtFixedRate(new TimerTask() {
//execute this every 10 ms
@Override
public void run() {
if(btnNewButton.getX() == x & btnNewButton.getY() == y) {
this.cancel();
}else if(btnNewButton.getX()<x){
btnNewButton.setLocation(btnNewButton.getX() + 1, btnNewButton.getY());
}else if(btnNewButton.getX()>x){
btnNewButton.setLocation(btnNewButton.getX() - 1, btnNewButton.getY());
}else if(btnNewButton.getY()<y){
btnNewButton.setLocation(btnNewButton.getX(), btnNewButton.getY()+1);
}else if(btnNewButton.getY()>y){
btnNewButton.setLocation(btnNewButton.getX(), btnNewButton.getY()-1);
}
}
}, 0, 1);
}
});
btnNewButton.setBounds(100, 100, 113, 36);
contentPane.add(btnNewButton);
}
}2.인스턴스 생성될 때 마다 시리얼넘버 부여
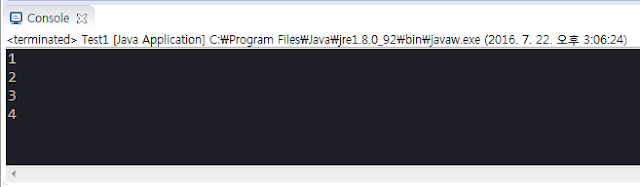
public class Test1 {
static int count;
int serialNo;
{
count++;
serialNo=count;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Test1 t1 = new Test1();
Test1 t2 = new Test1();
Test1 t3 = new Test1();
Test1 t4 = new Test1();
System.out.println(t1.serialNo);
System.out.println(t2.serialNo);
System.out.println(t3.serialNo);
System.out.println(t4.serialNo);
}
}3. 변수 초기화 순서
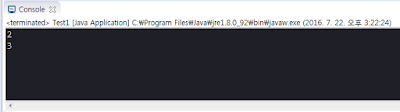
public class Test1 {
static int cv =1; //스태틱 변수 ----1 번째: 클래스가 메모리에 로딩될 떄 수행됨
int iv =1; //인스턴스 변수 ----3 번째: 인스턴스를 생성할 때 수행됨
static{ cv=2;} //스태틱 블럭 ----2 번째: 클래스가 메모리에 로딩될 떄 수행됨
{ iv=2;} //인스턴스 블럭 ----4 번째: 인스턴스를 생성할 때 수행됨
Test1(){ iv=3; } //생성자 ----5 번째: 인스턴스를 생성할 때 수행됨
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(cv); //스태틱 변수는 인스턴스 생성하지 않아도 프린트 할 수 있음
System.out.println(new Test1().iv); //인스턴스 변수는 인스턴스를 생성해야 프린트 가능함
}
}4
//참조변수가 참조하는 방식
class Test0{
static int cv =1; //스태틱 변수
int iv =1; //인스턴스 변수
static{ cv=2;} //스태틱 블럭
{ iv=2;} //인스턴스 블럭
Test0(){ iv=3; } //생성자
static void method1(){ //스태틱 메서드
System.out.println("static method1");
}
void method2(){ //인스턴스 메서드
System.out.println("instance method2");
}
void method3(){}
}
class Test0son extends Test0{
static int cv =100; //스태틱 변수
int iv =100; //인스턴스 변수
static{ cv=200;} //스태틱 블럭
{ iv=200;} //인스턴스 블럭
Test0son(){ iv=300; } //생성자
static void method1(){ //스태틱 메서드
System.out.println("static method1 son");
}
void method2(){ //인스턴스 메서드
System.out.println("instance method2 son");
}
void method3(){
System.out.println("super cv= "+super.cv);
System.out.println("super iv= "+super.iv);
System.out.print("super method1= ");
super.method1();
System.out.print("super method2= ");
super.method2();
}
}
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Test0.method1();
Test0son.method1();
new Test0().method2();
new Test0son().method2();
System.out.println(Test0.cv);
System.out.println(Test0son.cv);
System.out.println(new Test0().iv);
System.out.println(new Test0son().iv);
System.out.println();
Test0 ts0_ts0 = new Test0();
Test0 ts0_ts0son = new Test0son(); //참조변수를 부모클래스로 설정
ts0_ts0.method1();
ts0_ts0son.method1(); //스태틱 메서드는 참조변수를 따름
ts0_ts0.method2();
ts0_ts0son.method2(); //인스턴스 메서드는 ★★★★★인스턴스를 따름
System.out.println(ts0_ts0.cv);
System.out.println(ts0_ts0son.cv); //스태틱 변수는 참조변수를 따름
System.out.println(ts0_ts0.iv);
System.out.println(ts0_ts0son.iv); //인스턴스 변수는 ★★★★★참조변수를 따름
System.out.println();
ts0_ts0son.method3(); //부모의 인스턴스 메서드를 부를 수 있음(super 사용)
//인스턴스 메서드가 부모를 override하지만 super 통해 부를 수 있음
}
}5
//형변환으로 숨겨진 변수 불러오기
class Test0{
static int cv =1; //스태틱 변수
int iv =3; //인스턴스 변수
static void method1(){ //스태틱 메서드
System.out.println("static method1");
}
void method2(){ //인스턴스 메서드
System.out.println("instance method2");
}
}
class Test0son extends Test0{ //상속
static int cv =100;
int iv =300;
static void method1(){
System.out.println("static method1 son");
}
void method2(){
System.out.println("instance method2 son");
}
}
public class Exam01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Test0son ts1 = new Test0son();
ts1.method1();
((Test0)ts1).method1(); //형변환으로 부모의 스태틱 메서드 부름
ts1.method2();
((Test0)ts1).method2(); //오버라이드 된 부모의 인스턴스메서드를 불러올 수 없음★★★★
System.out.println(ts1.iv);
System.out.println(((Test0)ts1).iv); //형변환으로 부모의 인스턴스 변수 부름
System.out.println(ts1.cv);
System.out.println(((Test0)ts1).cv); //형변환으로 부모의 스태틱 변수 부름
Test0 ts0 = new Test0son();
ts0.method1();
((Test0son)ts0).method1(); //형변환을 통해 자식의 스태틱 메서드를 호출 할 수 있음
ts0.method2();
((Test0)ts0).method2(); //오버라이드 된 부모의 인스턴스메서드를 불러올 수 없음
((Test0son)ts0).method2();
System.out.println(ts0.cv);
System.out.println( ((Test0son)ts0).cv); //형변환으로 자식의 스태틱 변수 부름
System.out.println(ts0.iv);
System.out.println( ((Test0son)ts0).iv); //형변환으로 자식의 인스턴스 변수 부름
System.out.println();
}
}


댓글 없음:
댓글 쓰기